Lapsurgery.com.au, Gastric Bypass Surgery An Overview – Gastric bypass surgery is a weight-loss procedure primarily designed for individuals who struggle with severe obesity and related health issues. It involves altering the digestive system to help patients consume fewer calories and absorb fewer nutrients, leading to significant weight loss over time. As one of the most common types of bariatric surgery, gastric bypass has proven effective in helping patients achieve and maintain substantial weight loss, improve health conditions, and enhance quality of life.
What is Gastric Bypass Surgery?
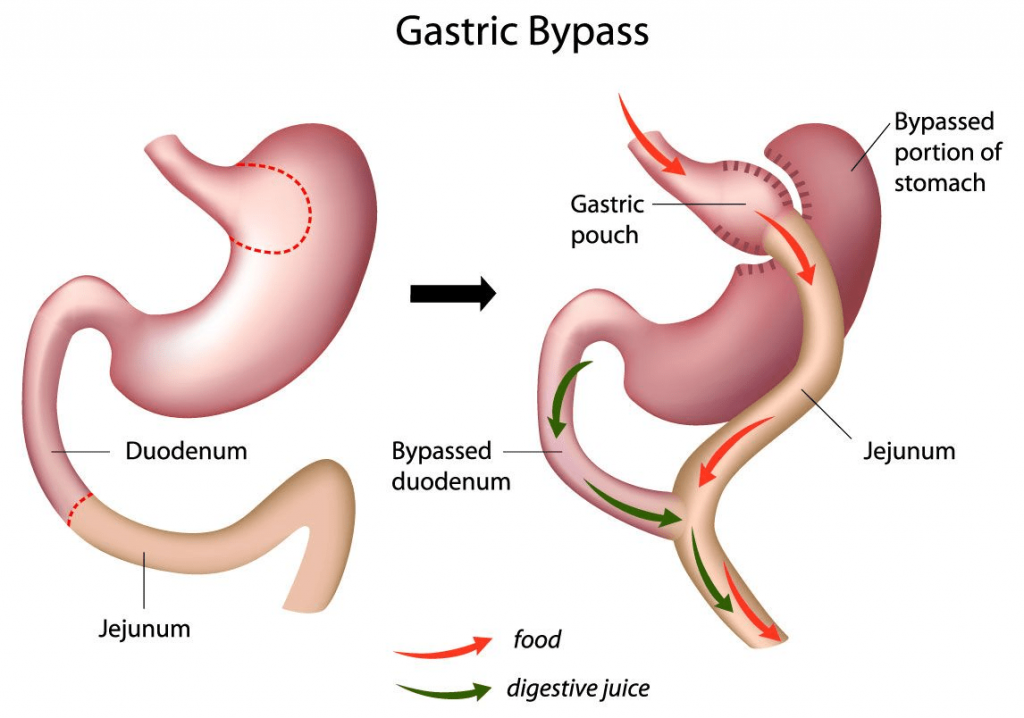
Gastric bypass surgery, technically called Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is a procedure that reduces the size of the stomach and reroutes part of the digestive system. In this surgery, a small pouch is created from the stomach, significantly reducing its size. This pouch is then connected directly to the small intestine, bypassing a large part of the stomach and the first section of the small intestine (duodenum). The surgery essentially restricts food intake and reduces calorie and nutrient absorption.
How Does Gastric Bypass Work?
Gastric bypass works in two main ways:
- Restricting Stomach Size: By creating a small stomach pouch, the procedure limits the amount of food the patient can eat at one time. Patients feel full after consuming smaller meals, helping them to control portion sizes.
- Reducing Nutrient Absorption: The bypassed section of the small intestine reduces the absorption of calories and nutrients, which further contributes to weight loss.
Who is a Candidate for Gastric Bypass?
Typically, candidates for gastric bypass surgery include individuals who:
- Have a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher (extreme obesity).
- Have a BMI of 35 or higher and suffer from obesity-related conditions like type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or sleep apnea.
- Have tried and been unsuccessful in losing weight through traditional methods such as diet and exercise.
- Are willing to make lifelong changes to their diet and lifestyle post-surgery.
Benefits of Gastric Bypass Surgery
For many patients, gastric bypass offers significant health and lifestyle benefits, including:
- Substantial and Sustained Weight Loss: Patients typically lose 60-80% of their excess weight within two years of surgery.
- Improvement or Resolution of Health Conditions: Many obesity-related health issues, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and sleep apnea, improve significantly after surgery.
- Increased Mobility and Quality of Life: Reduced weight allows for greater physical mobility, which can improve overall quality of life and psychological well-being.
- Lower Risk of Obesity-Related Complications: By achieving a healthier weight, patients reduce their risk of future health complications linked to obesity.
Risks and Complications
While gastric bypass is a generally safe procedure, it does carry certain risks and potential complications, including:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Due to reduced nutrient absorption, patients may develop deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, such as iron, calcium, and vitamin B12, requiring lifelong supplementation.
- Dumping Syndrome: A condition where food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, causing symptoms like nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and diarrhea.
- Infection and Surgical Complications: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection, blood clots, and complications related to anesthesia.
- Ulcers and Bowel Obstruction: Some patients may develop ulcers or blockages in the digestive tract, requiring additional medical intervention.
The Recovery Process
Recovery from gastric bypass surgery typically involves:
- Hospital Stay: Most patients remain in the hospital for 2-3 days post-surgery to monitor for complications.
- Gradual Diet Progression: Patients start with a liquid diet, gradually progressing to soft foods, and eventually solid foods over several weeks. This transition helps the stomach adapt to its new size.
- Lifestyle Changes: A successful outcome from gastric bypass requires lifelong lifestyle changes, including portion control, mindful eating, and regular exercise.
- Regular Follow-ups: Ongoing monitoring by healthcare providers is crucial to track progress, manage any complications, and adjust vitamin and mineral supplementation as needed.
Expected Results and Long-Term Success
Gastric bypass surgery has one of the highest success rates among bariatric procedures, with patients experiencing substantial weight loss and health improvements. Many patients maintain weight loss long-term, though it requires commitment to lifestyle and dietary adjustments. With adherence to post-surgery guidelines, the majority of patients see lasting positive effects on their health and quality of life.
Psychological and Emotional Aspects of Gastric Bypass
Gastric bypass surgery not only brings physical changes but also deeply impacts emotional and psychological health. Many patients experience a sense of renewed confidence and self-esteem as they lose weight and gain greater physical mobility. However, the adjustment can also be challenging, and it’s common to experience a range of emotions during the post-surgery period. Some considerations include:
- Mental Health Support: Because significant weight loss can be psychologically taxing, counseling and support groups can be invaluable. Many healthcare teams include mental health professionals to help patients cope with the adjustment and stay motivated.
- Body Image and Adjustment: As the body undergoes rapid changes, patients may struggle with body image issues or dissatisfaction even after achieving weight loss. Support groups and counseling can help address these feelings and create a positive body image.
- Managing Emotional Eating: Many people with obesity have used food as a coping mechanism. Learning new ways to manage emotions without turning to food is often a critical aspect of post-surgical care and long-term success.
Diet and Nutrition Post-Surgery
Following a gastric bypass, dietary changes are not just recommended they’re essential. The new stomach size and rerouted digestive pathway mean that the body’s ability to absorb nutrients is reduced, so patients must follow a strict diet to avoid complications. Key dietary adjustments include:
- Smaller, Frequent Meals: Due to the reduced stomach size, patients are advised to eat smaller portions and avoid large meals. Eating slowly and chewing thoroughly also help to avoid digestive issues.
- Focus on Protein: Protein becomes a dietary priority, as it aids in muscle maintenance and overall health. Common sources include lean meats, eggs, tofu, and beans.
- Vitamin and Mineral Supplements: Supplements are typically required to prevent nutrient deficiencies. This often includes multivitamins, calcium, vitamin D, iron, and vitamin B12. Regular blood tests help monitor these levels and adjust supplementation as needed.
- Avoiding Certain Foods: Sugary and high-fat foods can lead to “dumping syndrome” and cause discomfort. Carbonated drinks, alcohol, and caffeine are also discouraged, as they can irritate the stomach or lead to dehydration.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is crucial after gastric bypass surgery, helping to enhance weight loss, improve cardiovascular health, and prevent muscle loss. Some recommendations include:
- Start Slowly: After surgery, patients should gradually ease into physical activity. Walking and light stretching are often recommended in the initial recovery period.
- Progressive Strength Training: Building muscle helps support weight loss and improves metabolism. Gradually incorporating strength training into a routine can be effective.
- Long-Term Activity Commitment: Maintaining regular exercise (150 minutes of moderate activity per week) is essential for long-term weight management. Activities like swimming, cycling, yoga, and resistance exercises are often helpful options.
Long-Term Follow-Up and Health Monitoring
Gastric bypass surgery requires ongoing medical follow-up to ensure health and prevent complications. This long-term monitoring helps track weight loss progress, manage potential nutritional deficiencies, and address any emerging health issues. Typical follow-up care includes:
- Regular Check-ups: Patients often have frequent check-ups during the first year post-surgery to monitor their recovery, adjust supplements, and evaluate progress. After that, annual or semi-annual visits are common.
- Blood Tests and Screening: Routine blood tests help check for nutrient deficiencies, assess kidney and liver function, and monitor blood glucose levels.
- Supportive Services: Nutritional counseling, mental health support, and exercise coaching may be provided to assist patients in maintaining their new lifestyle.
Potential Alternatives to Gastric Bypass
For individuals who may not be ideal candidates for gastric bypass, other bariatric surgery options exist, such as:
- Gastric Sleeve Surgery: Also known as sleeve gastrectomy, this procedure reduces the stomach size by about 80%, forming a small, sleeve-like stomach. It restricts food intake but doesn’t significantly affect nutrient absorption.
- Adjustable Gastric Banding: Also called a “lap band,” this procedure places an adjustable band around the upper part of the stomach, creating a small pouch. It’s a reversible and less invasive option, though weight loss results are often more gradual.
- Duodenal Switch: This procedure combines a gastric sleeve with an intestinal bypass. It’s effective for extreme cases of obesity but carries higher risks of complications.
- Patients should discuss these options with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable choice based on their medical history, weight loss goals, and lifestyle.
Success Stories and Testimonials
Many individuals who have undergone gastric bypass surgery report significant life changes. Common themes in their testimonials include newfound energy, the ability to engage in activities previously limited by weight, and the improvement or even resolution of chronic health issues like diabetes and high blood pressure. Although every journey is unique, the collective experiences emphasize the importance of perseverance, discipline, and the support of family, friends, and medical professionals.
Conclusion
Gastric bypass surgery is a life-changing procedure for individuals facing severe obesity and related health challenges. While it involves certain risks and necessitates a lifelong commitment to lifestyle changes, the potential benefits in terms of weight loss, health improvement, and quality of life are profound. Patients considering this option should consult with a qualified bariatric surgeon to evaluate their suitability for the procedure and to fully understand both the risks and benefits involved.

