Lapsurgery.com.au, Managing Hernia Effective Treatment Approaches – Hernia is a medical condition characterized by the protrusion of an organ or tissue through a weakened spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. While surgery is often the primary treatment, several approaches and lifestyle modifications contribute to effective hernia management.
Diagnosis and Assessment
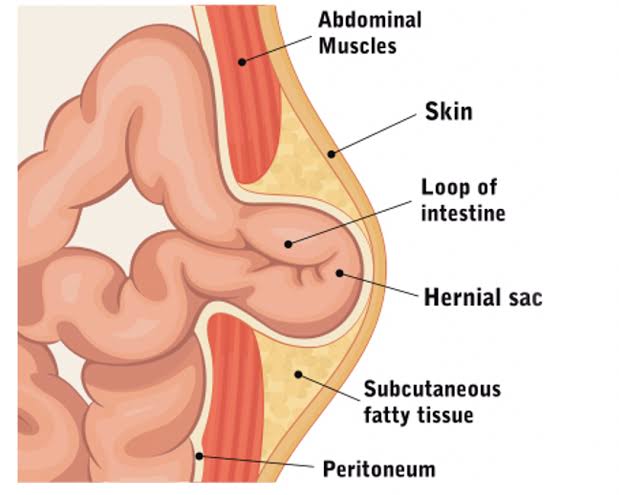
Identifying the type of hernia is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan. Common types include inguinal, femoral, umbilical, and hiatal hernias.
Medical professionals typically use imaging studies, such as ultrasound or CT scans, to diagnose and assess the severity of the hernia.
Lifestyle Modifications
Dietary Changes: Adopting a high-fiber diet can prevent constipation, reducing strain during bowel movements and minimizing pressure on weakened muscles.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is essential to alleviate strain on the abdominal wall and reduce the risk of hernia recurrence.
Non-surgical Management
Supportive Garments: Wearing abdominal binders or trusses can provide temporary relief and support, especially for smaller hernias.
Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises may help strengthen the surrounding muscles, offering additional support to the weakened area.
Surgical Options
Open Hernia Repair: This traditional method involves making an incision directly over the hernia site to push the protruding tissue back into place and reinforce the muscle with stitches or mesh.
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair: Minimally invasive surgery utilizing small incisions and a camera for guidance.
Surgeons insert a mesh to strengthen the weakened area, often resulting in quicker recovery times.
Postoperative Care
Following surgery, patients must adhere to guidelines provided by their healthcare team, including restrictions on physical activities and proper wound care.
Early mobilization is encouraged to prevent complications and promote a faster recovery.
Complications and Follow-up
Complications, although rare, may include infection, recurrence, or chronic pain. Regular follow-up appointments allow healthcare providers to monitor progress and address any concerns promptly.
Preventive Measures
Incorporating core-strengthening exercises into daily routines can help prevent hernias.
Addressing risk factors, such as chronic coughing or heavy lifting, can minimize the likelihood of developing hernias.
Closing
In conclusion, the treatment of hernias involves a combination of surgical and non-surgical approaches. It is crucial for individuals to collaborate closely with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on the type and severity of the hernia.

