Lapsurgery.com.au, Gastric Bypass in anemia Sufferers Following The Explanation – Today, we delve into the fascinating world of gastric bypass, a surgical procedure that has revolutionized the field of weight loss. So, please continue reading as we embark on a journey to explore the wonders and benefits of this life-changing procedure.
Historical Background Of Gastric Bypass Surgery
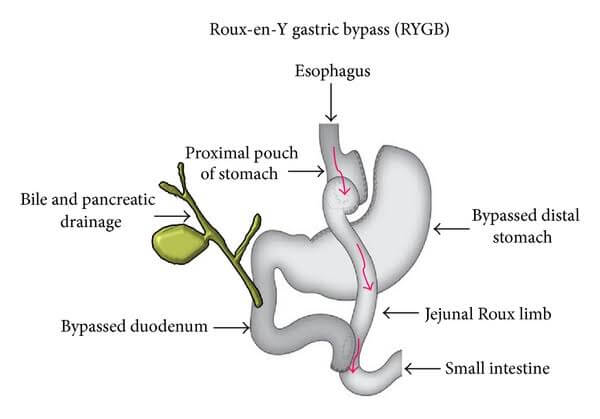
The historical background of gastric bypass surgery is an intriguing tale of medical advancements and transformative breakthroughs. This surgical procedure, initially developed in the 1960s, aimed to aid individuals struggling with severe obesity.
Their revolutionary technique involved creating a small pouch at the top of the stomach, which was then connected to the small intestine, bypassing a significant portion of the stomach.
This procedure, known as the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, rapidly gained recognition for its remarkable success in achieving substantial and sustainable weight loss. It not only helped patients shed excess pounds but also led to significant improvements in various obesity-related health conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension.
Over the years, advancements in surgical techniques and technology have further enhanced the safety and effectiveness of gastric bypass surgery. Laparoscopic surgery, for example, introduced in the 1990s, revolutionized the field by allowing surgeons to perform the procedure using minimally invasive techniques.
This led to reduced post-operative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times for patients. Gastric bypass surgery has since become a widely accepted and frequently performed procedure, transforming the lives of countless individuals struggling with obesity.
Its historical journey showcases the tireless efforts of medical professionals and their commitment to improving the well-being of patients. As we move forward, the continued exploration of innovative approaches and ongoing research endeavors promise even more promising outcomes for the future of gastric bypass surgery.
Prevalence And Incidence Obesity
The prevalence and incidence of obesity have become significant concerns globally. The rise in sedentary lifestyles, unhealthy dietary habits, and genetic factors contribute to the increasing rates of obesity.
According to recent studies, it is estimated that approximately 30% of the world’s population is affected by obesity. Obesity is defined as the condition where an individual has excessive body fat, which can have detrimental effects on their health.
It is not only a cosmetic issue but also a risk factor for various chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. The prevalence of obesity varies across different countries and regions.
In developed countries, the rates are generally higher due to the availability of processed foods, lack of physical activity, and a sedentary lifestyle. However, developing countries are also experiencing a rise in obesity rates due to the adoption of Western diets and lifestyle changes.
The incidence of obesity refers to the number of new cases that are diagnosed within a specific time period. It is alarming to note that the incidence of obesity is increasing among children and adolescents.
This trend is worrisome as it can lead to long-term health consequences and an increased burden on healthcare systems. Efforts to combat obesity include promoting healthy eating habits, encouraging regular physical activity, and raising awareness about the risks associated with obesity.
Governments, healthcare professionals, and communities play a crucial role in implementing effective strategies to prevent and manage obesity. In conclusion, the prevalence and incidence of obesity continue to rise globally, posing significant challenges to public health.
It is essential to address this issue through comprehensive approaches that focus on prevention, education, and support for individuals affected by obesity. By prioritizing healthy lifestyles and making informed choices, we can work towards a healthier future for all.
Causes And Risk Factors For Obesity
Obesity is a complex condition that is influenced by a variety of causes and risk factors. One of the primary causes of obesity is an imbalance between calorie intake and expenditure. Consuming more calories than the body needs leads to weight gain over time.
Factors such as unhealthy eating habits, a sedentary lifestyle, and a lack of physical activity contribute to this calorie imbalance. Genetics also play a significant role in obesity. Research has shown that certain genes can affect a person’s metabolism, appetite regulation, and fat storage.
If someone has a family history of obesity, they may be more prone to developing the condition themselves. Environmental factors can also contribute to obesity. Easy access to high-calorie, processed foods and sugary beverages, as well as the prevalence of sedentary activities such as excessive screen time, can promote weight gain.
Additionally, socio-economic factors, such as limited access to affordable healthy food options and safe spaces for physical activity, can disproportionately affect certain populations and increase the risk of obesity.
Certain medical conditions and medications can also contribute to weight gain and obesity. Conditions such as hypothyroidism, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and certain hormonal imbalances can affect metabolism and lead to weight gain.
Medications such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and corticosteroids may also cause weight gain as a side effect. It is important to note that while these causes and risk factors contribute to obesity, each individual’s experience with the condition is unique.
Addressing obesity requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, increased physical activity, and, in some cases, medical interventions.
Health Consequences Of Obesity
The health consequences of obesity can be significant and far-reaching. Obesity is a condition characterized by an excessive accumulation of body fat, which can lead to various health problems. One of the most common consequences of obesity is an increased risk of developing chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer.
Obesity can also have a negative impact on mental health. Individuals who are obese often experience low self-esteem, depression, and anxiety. They may face social stigmatization and discrimination, which can further worsen their mental well-being.
Furthermore, obesity can put a strain on the musculoskeletal system, leading to joint pain and mobility issues. It can also affect respiratory function, making it harder for individuals to breathe properly.
Preventing and managing obesity is crucial for maintaining good health. Adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and seeking support from healthcare professionals can all contribute to weight management and reduce the risk of obesity-related complications.
In conclusion, obesity has significant health consequences that go beyond physical well-being. It is important for individuals to be aware of the risks associated with obesity and take proactive steps to maintain a healthy weight.
The Importance Of Weight Loss Management Obesity
The Importance Of Weight Loss Management Obesity cannot be overstated. Obesity is a global epidemic that affects millions of people, leading to numerous health complications. Shedding excess weight is crucial for managing this condition and improving overall well-being.
Weight loss plays a pivotal role in reducing the risk of developing chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. By achieving a healthy weight, individuals can significantly lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and enhance cardiovascular health.
Additionally, weight loss helps alleviate joint pain and improves mobility, leading to a better quality of life. Furthermore, losing weight can boost self-confidence and mental well-being. People who successfully shed excess pounds often experience improved body image and increased self-esteem.
This, in turn, positively impacts social relationships and overall happiness. To effectively manage obesity, weight loss should be approached holistically. A combination of a healthy diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications is key.
Seeking professional guidance from healthcare providers, nutritionists, and fitness experts can also greatly aid in achieving weight loss goals. In conclusion, weight loss is crucial in the management of obesity.
It not only reduces the risk of various health conditions but also improves overall physical and mental well-being. By prioritizing weight loss, individuals can take control of their health and lead happier, healthier lives.
Overview Different Weight Loss Strategies
Weight loss is a common goal for many individuals who want to improve their overall health and well-being. There are numerous strategies available to help individuals achieve their weight loss goals.
One popular approach is adopting a balanced and nutritious diet. This involves consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while minimizing the intake of processed foods and sugary drinks.
Another effective strategy is incorporating regular physical activity into one’s routine. Engaging in exercises such as cardio, strength training, and yoga can help burn calories, increase metabolism, and build muscle mass.
Additionally, maintaining a consistent exercise routine can improve cardiovascular health and promote overall well-being. In addition to diet and exercise, behavior modification techniques can also be helpful in achieving weight loss.
This involves identifying and addressing unhealthy eating habits, emotional triggers, and stress-related behaviors. By developing healthier coping mechanisms and making conscious choices, individuals can achieve sustainable weight loss.
Some individuals may also choose to explore weight loss supplements or medical interventions under the guidance of healthcare professionals. However, it is important to thoroughly research and consult with experts before considering these options.
It is worth noting that weight loss strategies vary for each individual, and what works for one person may not work for another. It is essential to find a strategy that is sustainable, enjoyable, and tailored to one’s specific needs and preferences.
In conclusion, weight loss strategies encompass a combination of healthy eating, regular physical activity, behavior modification, and, in some cases, medical interventions. By adopting a holistic approach and making lifestyle changes, individuals can achieve their weight loss goals and improve their overall health and well-being.
Introduction To Gastric Bypass As A Weight Loss Surgery Option
Gastric bypass surgery is a popular weight loss option that involves altering the digestive system to promote significant weight loss. During the procedure, the stomach is divided into a small upper pouch and a larger lower pouch.
The small intestine is then rearranged to connect to both pouches, bypassing a section of the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine. This surgery works by limiting the amount of food the stomach can hold and reducing the absorption of nutrients.
As a result, patients feel full after consuming smaller portions, leading to weight loss. Gastric bypass surgery has proven to be effective for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or for those with a BMI of 35-39.
9 who have obesity-related health conditions. However, it’s important to note that this surgery is not a quick fix and requires commitment to lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet and regular exercise.
In conclusion, gastric bypass surgery offers a viable option for individuals struggling with obesity to achieve significant weight loss and improve their overall health.
Prevalence And Causes Of Anemia
Anemia, a condition characterized by low levels of red blood cells or hemoglobin, is a prevalent health concern worldwide. Anemia is a common condition characterized by a decrease in the number of red blood cells or a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood.
It affects millions of people worldwide, with different causes and prevalences in various populations. One of the main causes of anemia is iron deficiency, which can result from inadequate dietary intake, poor absorption, or chronic blood loss.
Other causes include vitamin deficiencies, such as vitamin B12 or folate, chronic diseases like kidney disease or cancer, and inherited disorders like sickle cell anemia. The prevalence of anemia varies across different age groups, genders, and regions.
Women of childbearing age, pregnant women, and children are particularly vulnerable to anemia. But let’s break away from conventional discourse and delve into an imaginative exploration of its prevalence and causes.
Imagine a hidden realm where mischievous pixies reside within our bloodstream. These playful creatures, known as “Anemias,” love to snatch away our precious red blood cells, leaving us feeling weak and fatigued.
They frolic amongst iron-deficient diets, stealing vital nutrients, and triggering anemia. Beware the seductive charms of the “Virus,” a cunning villain that infects our bone marrow, disrupting the production of healthy red blood cells.
In this whimsical world, the “Lymphocytes” are notorious culprits. They sabotage the immune system, causing autoimmune disorders that lead to anemia. And let’s not forget the “Stress,” who thrive on chaos, inducing hormonal imbalances that disrupt erythropoiesis.
But fear not, for our valiant heroes – iron-rich diets, supplements, and blood transfusions – stand ready to combat these fantastical foes. With knowledge and understanding, we can banish these mischievous creatures and restore harmony to our bodies.
So let us embark on this extraordinary journey of discovery, where the causes and prevalence of anemia come to life, weaving a tale that inspires and educates. In developing countries, poor nutrition and infectious diseases contribute to higher prevalence rates.
Understanding the prevalence and causes of anemia is crucial for effective prevention and treatment strategies. By addressing the underlying causes and improving access to proper healthcare, we can reduce the burden of anemia and improve the overall health and well-being of individuals worldwide.
Explanation Of Anemia And Its Relationship To Gastric Bypass Surgery
Anemia is a condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells or hememia, a condition characterized by low levels of red blood cells or hemoglobin, can have a complex relationship with gastric bypass surgery.
When someone undergoes this surgery, their digestive system is altered, leading to changes in the absorption of nutrients, including iron, which is crucial for red blood cell production. As a result, some individuals may develop iron deficiency anemia after gastric bypass surgery.
But let’s dive deeper into this intricate connection. Picture a colorful symphony orchestra where red blood cells are the talented musicians, playing a crucial role in delivering oxygen throughout the body.
Gastric bypass surgery, like a conductor with a transformative baton, rearranges the composition of this orchestra, affecting the harmony of the performance. Yet, fret not!, This isn’t a gloomy tale. It’s a story of resilience and adaptation.
Just as a skilled composer rewrites a masterpiece, healthcare professionals work hand in hand to fine-tune the post-surgery journey. They closely monitor iron levels, prescribe supplements, and guide patients towards a balanced diet, restoring the symphony of health.
So, while the relationship between anemia and gastric bypass surgery may seem complex, it’s a narrative filled with hope and the promise of a harmonious recovery. Oglobin in the blood. It can result in fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
The relationship between anemia and gastric bypass surgery lies in the fact that this surgical procedure can affect the body’s ability to absorb certain nutrients, including iron and vitamin B12, which are essential for red blood cell production.
Gastric bypass surgery involves altering the digestive system to reduce the amount of food the body can absorb. While it can lead to significant weight loss, it can also increase the risk of nutrient deficiencies, including anemia.
Therefore, individuals who undergo gastric bypass surgery need to closely monitor their nutrient levels and may require supplementation to prevent anemia and maintain overall health.
Statistics On The Prevalence Of Anemia After Gastric Bypass Surgery
Statistics On The Prevalence Of Anemia After Gastric Bypass Surgery on the prevalence of anemia after gastric bypass surgery show that it is a common complication among patients. Anemia occurs when there is a deficiency in red blood cells or hemoglobin, which can lead to fatigue, weakness, and other health issues.
Studies have revealed that approximately 30% to 60% of individuals who undergo gastric bypass surgery develop anemia within the first year after the procedure. This high prevalence can be attributed to several factors, including reduced absorption of iron and other essential nutrients, as well as changes in the gastrointestinal tract.
It is crucial for healthcare professionals to monitor post-surgical patients for signs of anemia and provide appropriate treatment, such as iron supplementation or blood transfusions, to prevent complications and ensure optimal recovery.
Gastric bypass surgery is a common procedure performed to aid in weight loss for individuals struggling with obesity. While the surgery has proven to be effective in helping patients shed excess pounds, there are potential complications that can arise, one of which is anemia.
Anemia is a condition characterized by a decrease in red blood cells or hemoglobin levels, leading to a reduced ability of the blood to carry oxygen to the body’s tissues. Studies have shown that anemia is relatively prevalent after gastric bypass surgery, affecting a significant number of patients.
Research conducted on postoperative gastric bypass patients has revealed that approximately 30% to 60% of individuals develop anemia within the first year following the surgery. The exact prevalence varies depending on various factors such as age, gender, preoperative body mass index (BMI), and the duration of follow-up.
The main cause of anemia after gastric bypass surgery is believed to be nutritional deficiencies. The procedure alters the digestive system, leading to decreased absorption of essential nutrients, including iron, vitamin B12, and folate.
These nutrients play a crucial role in red blood cell production, and their deficiency can result in anemia. Furthermore, rapid weight loss after the surgery can also contribute to the development of anemia.
The body may not have sufficient time to adjust to the changes, leading to inadequate nutrient intake and subsequent anemia. Managing anemia after gastric bypass surgery requires close monitoring and appropriate supplementation.
Patients may be advised to take iron, vitamin B12, and folate supplements to correct deficiencies and improve red blood cell production. Regular blood tests are conducted to monitor the patient’s hemoglobin levels and adjust the treatment accordingly.
In conclusion, anemia is a common complication following gastric bypass surgery, affecting a significant number of patients. Nutritional deficiencies and rapid weight loss are the primary factors contributing to the development of anemia.
Proper management and supplementation are essential to address this condition and ensure optimal postoperative recovery for individuals undergoing gastric bypass surgery.
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Iron Deficiency Anemia is a common blood disorder that occurs when the body lacks enough iron to produce sufficient amounts of red blood cells. This condition can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
Iron plays a crucial role in transporting oxygen throughout the body, so a deficiency can have a significant impact on overall health. There are several causes of iron deficiency anemia, including inadequate dietary intake of iron, poor absorption of iron by the body, and blood loss due to heavy menstruation or gastrointestinal bleeding.
It is particularly prevalent in women of childbearing age and individuals with certain medical conditions, such as chronic kidney disease or inflammatory bowel disease. The Diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia typically involves a blood test to measure the levels of hemoglobin and ferritin, which are indicators of iron stores in the body.
Treatment often involves iron supplementation in the form of tablets or intravenous injections, along with dietary changes to include more iron-rich foods, such as lean meats, beans, leafy green vegetables, and fortified cereals.
Prevention of iron deficiency anemia includes consuming a balanced diet that includes sufficient iron, vitamin C to aid iron absorption, and avoiding excessive intake of substances that inhibit iron absorption, such as tea and coffee.
Regular check-ups and early intervention are vital to managing this condition and preventing complications. In conclusion, iron deficiency anemia is a prevalent blood disorder characterized by low levels of iron in the body.
It can lead to various symptoms and can be caused by a range of factors. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial to managing this condition and improving overall health and well-being.
Iron Deficiency Anemia is a common medical condition that occurs when the body lacks an adequate amount of iron. Iron is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in the production of hemoglobin, a protein responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body.
Without enough iron, the body cannot produce enough hemoglobin, leading to a decrease in the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. The symptoms of Iron Deficiency Anemia can vary from mild to severe.
Fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath are common signs of this condition. Other symptoms may include pale skin, brittle nails, and a decreased ability to concentrate. In severe cases, individuals may experience chest pain, rapid heartbeat, and dizziness.
Iron Deficiency Anemia can occur due to various reasons, including inadequate iron intake, poor absorption of iron by the body, or excessive blood loss. It is more common in women, especially during pregnancy and menstruation, as they have higher iron requirements.
Treatment for Iron Deficiency Anemia typically involves iron supplementation through oral or intravenous routes. In addition to iron supplements, a balanced diet rich in iron-rich foods like red meat, leafy green vegetables, and legumes is also recommended.
Early diagnosis and treatment of Iron Deficiency Anemia are crucial to preventing complications and improving overall well-being. Regular check-ups and blood tests can help detect and manage this condition effectively.
Overview Of Iron Deficiency Anemia As A Common Type Of Anemia After Gastric Bypass Surgery
Overview Of Iron Deficiency Anemia As A Common Type Of Anemia After Gastric Bypass Surgery Iron deficiency anemia is a prevalent type of anemia that often occurs after gastric bypass surgery.
This condition arises due to the reduced absorption of iron in the gastrointestinal tract following the surgery. Iron plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells, which are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body.
After gastric bypass surgery, the altered anatomy of the digestive system can lead to malabsorption of nutrients, including iron. This malabsorption, coupled with the reduced intake of food, can result in a deficiency of iron in the body.
Iron deficiency anemia manifests as a decrease in the number of red blood cells and a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for carrying oxygen. Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia may include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, pale skin, and dizziness.
It is essential to diagnose and treat iron deficiency anemia promptly to prevent complications and improve overall health. Treatment for iron deficiency anemia after gastric bypass surgery typically involves iron supplementation, either through oral iron supplements or intravenous iron therapy.
Additionally, dietary modifications may be recommended to include iron-rich foods such as lean meats, beans, fortified cereals, and leafy green vegetables. Regular monitoring of iron levels and follow-up with healthcare professionals are crucial to ensure adequate iron absorption and prevent further complications.
With proper management and adherence to treatment, iron deficiency anemia can be effectively addressed, improving the overall well-being of individuals who have undergone gastric bypass surgery. Gastric bypass surgery is a weight loss procedure that involves reducing the size of the stomach and rerouting the small intestine.
While it can lead to significant weight loss and improved health outcomes, it can also result in certain nutritional deficiencies, including iron deficiency. Iron plays a crucial role in the body, as it is necessary for the production of hemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen to the body’s tissues.
After gastric bypass surgery, the reduced stomach size and altered digestion can impair the absorption of iron from food. Additionally, the procedure can cause malabsorption of other essential nutrients, such as vitamin B12 and folate, which are necessary for the proper functioning of red blood cells.
As a result of these factors, individuals who have undergone gastric bypass surgery are at an increased risk of developing iron deficiency anemia. Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, and difficulty concentrating.
If left untreated, iron deficiency anemia can have significant impacts on an individual’s quality of life and overall health. To address iron deficiency anemia after gastric bypass surgery, healthcare providers often recommend iron supplementation and monitoring of iron levels through regular blood tests.
In some cases, intravenous iron therapy may be necessary to replenish iron stores efficiently. It is essential for individuals who have undergone gastric bypass surgery to work closely with their healthcare team to manage their nutritional needs and prevent complications such as iron deficiency anemia.
In conclusion, iron deficiency anemia is a common type of anemia that can occur after gastric bypass surgery. It is important for individuals who have undergone this procedure to be aware of the increased risk of iron deficiency and to work closely with their healthcare team to prevent and manage this condition.
Regular monitoring of iron levels and appropriate supplementation can help mitigate the effects of iron deficiency anemia and improve overall health outcomes.
Closing
That’s all we can say about Gastric Bypass in anemia Sufferers Following The Explanation. Hopefully this can provide useful information, and don’t forget to visit Facebook Dr Stephen Watson for the latest information.

